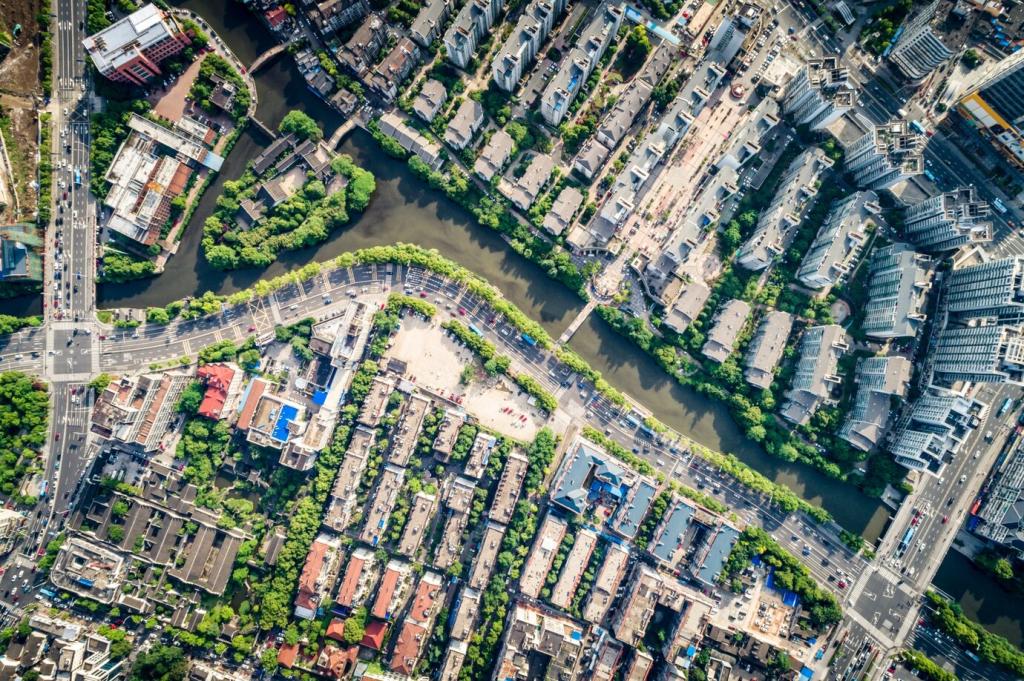
Native Plants as Living Infrastructure
Match sun, soil, and moisture to each native plant’s needs. Drought-tough grasses stabilize sunny strips, while shade-loving ferns soften courtyards. Ask your local native plant society for region-specific lists, and share your go-to species to help new restorers start strong.
Native Plants as Living Infrastructure
Build vertical structure: groundcovers, wildflowers, grasses, shrubs, and small trees. Stagger bloom times and berry seasons so nectar, seeds, and shelter persist through the year. This layered design welcomes butterflies, songbirds, and overwintering insects into even compact urban spaces.